Sin categoría
Cómo aprovechar las cámaras cardán para explorar recursos
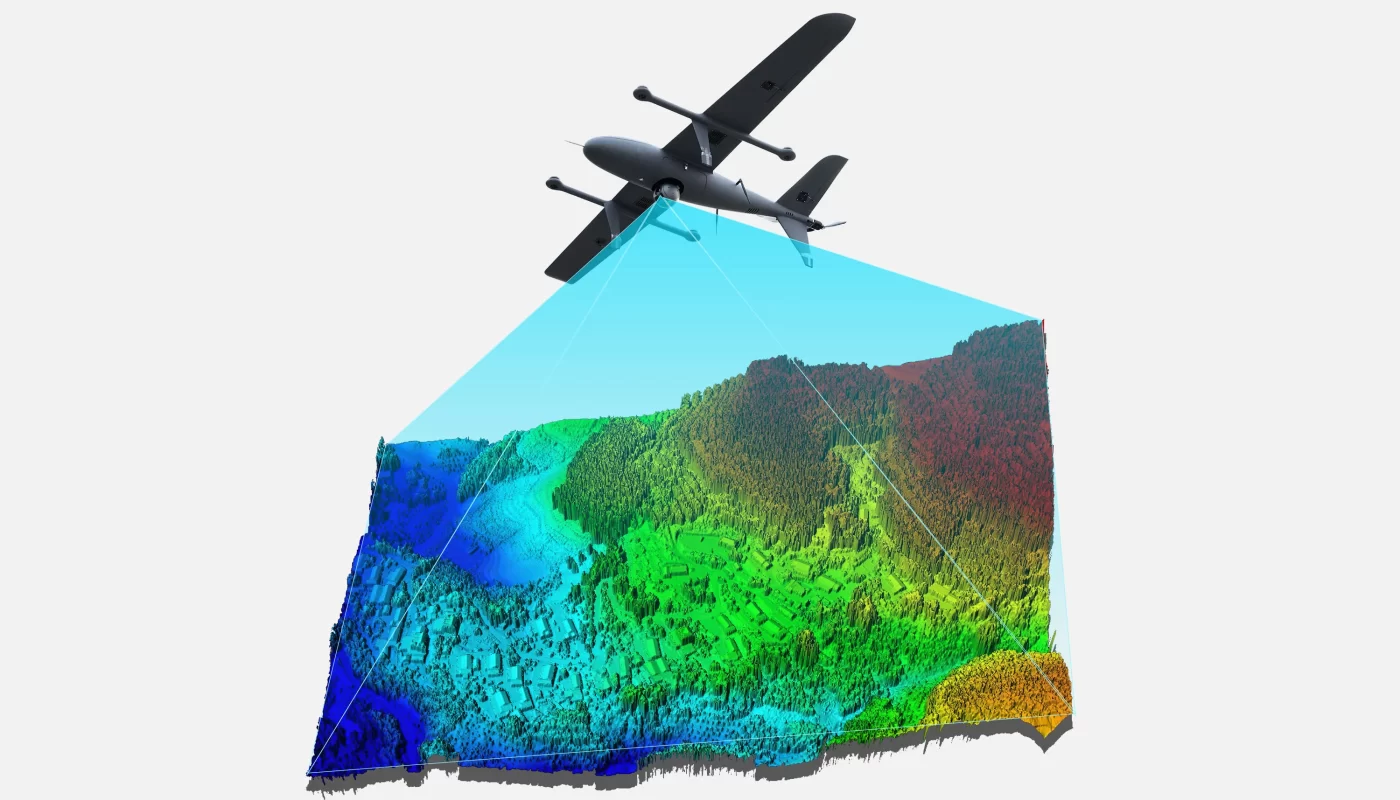
Gimbal camera technology is becoming increasingly essential in the field of resource exploration, particularly in industries such as mining, oil, and natural gas. When mounted on drones, helicopters, or other aerial platforms, gimbal cameras provide stable, high-resolution imaging that supports real-time data collection and improves the accuracy and efficiency of exploration work. Below are the key ways gimbal cameras are being utilized in resource exploration: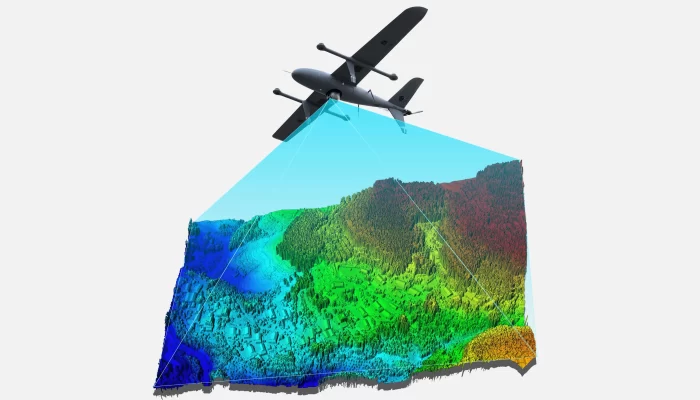
1. Geological Structure and Terrain Mapping
Gimbal cameras equipped with high-definition and multispectral imaging sensors can capture detailed visual data of the Earth’s surface. This enables geologists to analyze terrain features, rock formations, and surface cover more effectively. The clarity and stability of the captured imagery help identify changes in geological structures, the presence of mineral veins, and other potential resource indicators.
For example, in mineral exploration, gimbal-stabilized imaging systems produce detailed geological visuals, allowing geologists to pinpoint promising mineral zones more quickly and reduce exploration time.
2. Remote Sensing Data Acquisition and Interpretation
Gimbal cameras can be integrated with various remote sensing technologies, such as infrared, thermal, or multispectral sensors, to collect comprehensive data from target areas. These sensors can detect hidden indicators such as subsurface water flow or thermal anomalies, which often point to the presence of valuable resources.
For instance, thermal imaging can reveal hot spots in a survey area, which may signal underground mineral activity or geothermal potential.
3. Rapid and Large-Scale Area Surveys
Resource exploration often involves vast and remote regions, making traditional ground-based surveys costly and time-consuming. By deploying drones or aerial systems equipped with gimbal cameras, exploration teams can rapidly cover large areas and capture high-resolution imagery, greatly improving operational efficiency.
In oil exploration, for example, drones with gimbal-mounted cameras can quickly scan offshore or inaccessible zones, collecting detailed geological data to support drilling strategies.
4. Real-Time Observation and Strategic Adjustment
With the ability to stream live video and transmit real-time imagery, gimbal cameras allow exploration teams to monitor field conditions instantly. This capability enables early detection of resource-rich zones or potential hazards, allowing teams to adapt their strategies on the go and reduce the risk of errors.
For example, live feeds from gimbal cameras can help teams remotely assess ongoing exploration activities and make informed decisions without needing to be physically present on-site.
5. Environmental Impact Monitoring
Resource exploration can have significant environmental effects. Gimbal cameras provide a means to monitor and evaluate these impacts through aerial photography and video. Teams can analyze changes in land use, vegetation cover, or water bodies to ensure exploration activities are sustainable and environmentally responsible.
For instance, aerial footage captured by gimbal cameras can track changes in the ecosystem over time, helping identify whether additional protective measures are needed to minimize environmental disruption.
Conclusión
Gimbal camera technology significantly enhances the safety, precision, and efficiency of modern resource exploration. From geological mapping to environmental assessment, these cameras offer a flexible and reliable solution that enables better data collection, faster decision-making, and improved exploration outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, gimbal cameras are set to play an even more vital role in the future of resource exploration.